This article introduces the React Multiple Select using React Hooks.
I have vendors in various cities who are providing service to their customers. The situation is I need to assign societies to vendors as per their preference. A vendor may provide service to multiple societies in an area.
For this, I used Metronic theme and React hooks – useEffect.
There is a list of vendors and now I want to assign societies to a particular vendor.
To do so I redirected to details of the vendor.
First, select a city, then an area and then I want a filtered list of societies from that area of the city.
![]()
Step 1 :
Fetched a list of cities using async-await with useEffect hook.
/* Get list of all Cities */
const apiUrl = API_ENDPOINT + “city_list/”;
useEffect(() => {
const fetchData = async () => {
const result = await axios(apiUrl).then(response => response.data)
.then((data) => {
setData(data.data);
let count = Object.keys(data.data).length;
setcount(count);
})
};
fetchData();
}, []);
/* End Get list of all Cities */
Step 2 :
Fetched a list of areas from the selected city using async-await with useEffect as —>
/* Get area list by City */
const apiUrlArea = API_ENDPOINT + “area_list/”;
useEffect(() => {
let postAreaData=”;
if(formdata.city_id && formdata.city_id !==”){
postAreaData = {city_id:formdata.city_id}
const fetchData = async () => {
const result = await axios.post(apiUrlArea,postAreaData).then(response => response.data)
.then((data) => {
setareadata(data.data);
})
};
fetchData();
}
},[formdata.city_id]);
/* End Get area list by City */
Here formdata contains details of the vendor to edit.
This code will get executed as we change City and we are able to get a list of all areas from the selected city.
Step 3 :
Now I have a city and area , I can get a list of all societies in that area.
/* Get Societies by City & Area */
const apiUrlGetSociety = API_ENDPOINT + “society_list”;
useEffect(() => {
let postCityAreaData = {
area_id:formdata.area_id,
city_id:formdata.city_id,
}
const temp_slist = [];
if(formdata.area_id && formdata.area_id!== ” && formdata.city_id && formdata.city_id!== ” ){
const fetchData = async () => {
const result = await axios.post(apiUrlGetSociety,postCityAreaData).then(response => response.data)
.then((data) => {
data.data.forEach(element => {
const obj_temp = {‘id’:element.id, ‘name’:element.name};
temp_slist.push(obj_temp);
});
setAllSocieties(temp_slist);
setShowLoading(false);
console.log(“allSocieties”);
console.log(temp_slist);
})
};
fetchData();
}
},[formdata.area_id,formdata.city_id]);
/* End Get Societies of Area */
Here I get a list of societies as an array of object – {id,name}
let allSocieties = [ {“id”: 6,”name”: “Abhiruchi”}, {“id”: 2,”name”: “Sahara Society”}, {“id”: 3,”name”: “Satyam Society”},]
Now we have a filtered list of societies with respect to the area from the city.
Step 4 :
To show listing on form I used form-components from Metronics.
( https://keenthemes.com/metronic/preview/react/demo2/google-material/inputs/selects )
The Select component can handle multiple selections. It’s enabled with multiple property.
<FormControl className='form-control'>
<Select
multiple
name = “societies”
id = “societies”
value = { selectedSocieties }
onChange = { handleChange_multiple }
input = { <Input id=”select-multiple-chip” /> }
renderValue = { selected => (
<div className = {classes.chips}>
{ selected.map( s => {
const chipname = allSocieties.find(soc => soc.id === s);
return (chipname
? <Chip
key={s}
label={chipname.name}
className={classes.chip}
data-aaa={JSON.stringify(allSocieties)}
/>
: ”)
})}
</div>
)}
MenuProps={MenuProps}
>
{ allSocieties.map((itemsociety) => (
<MenuItem
key={itemsociety.id}
value={itemsociety}
>
<Checkbox checked={selectedSocieties.includes(itemsociety.id) } />
<ListItemText primary={itemsociety.name} />
</MenuItem>
))}
</Select>
</FormControl>
In the above select component, we have passed selectedSocieties to value attribute.
selectedSocieties is an array of ids of societies which are already assigned to vendor.
I can get list of assigned societies to vendor as –>
useEffect(() => {
setShowLoading(true)
setformdata(props.data)
if(props.data.vendorSociety && props.data.vendorSociety !== ” && props.data.vendorSociety !== ‘undefined’ ){
props.data.vendorSociety.forEach(el => {
const obj = {‘id’:el.id, ‘name’:el.name};
temp_selected_slist.push(el.id);
})
setSelectedSocieties(temp_selected_slist);
}
}, [props.data]);
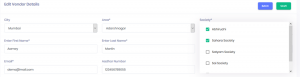
After selecting one/more societies, handleChange_multiple event bind selected societies data to selectedSocieties . See the following code:
const handleChange_multiple = event =>{
let newitems = event.target.value.filter(t => typeof t !== ‘number’);
let changed = newitems[0].id;
let cleanthis = event.target.value.filter(t => typeof t === ‘number’);
newitems.forEach(i => cleanthis.push(i.id));
const newSelectedItems = selectedSocieties.includes(changed)
? selectedSocieties.filter(v => v !== changed)
: […selectedSocieties, changed];
setSelectedSocieties(newSelectedItems);
}
In the example given in Metronic , handleChange event deals with an array of the name only. In above we are dealing with an array of objects.
In the above code, in handleChange_multiple event, we get newly selected items as an object – newitems {id,name}. Then extract id from it and saved to changed.
Now I can check with changed whether it exist in selectedSocieties.
const newSelectedItems = selectedSocieties.includes(changed)
? selectedSocieties.filter(v => v !== changed)
: […selectedSocieties, changed];
setSelectedSocieties(newSelectedItems);
In above article , we learned how to use multiple select in combination with array of objects and obtain required results.

